Microservice
A microservice architecture – A variant of the service-oriented architecture (SOA) – arranges an application as a collection of loosely-coupled services.
In a microservice architecture, services are fine-grained and the protocols are lightweight.
Monolit - Microservice
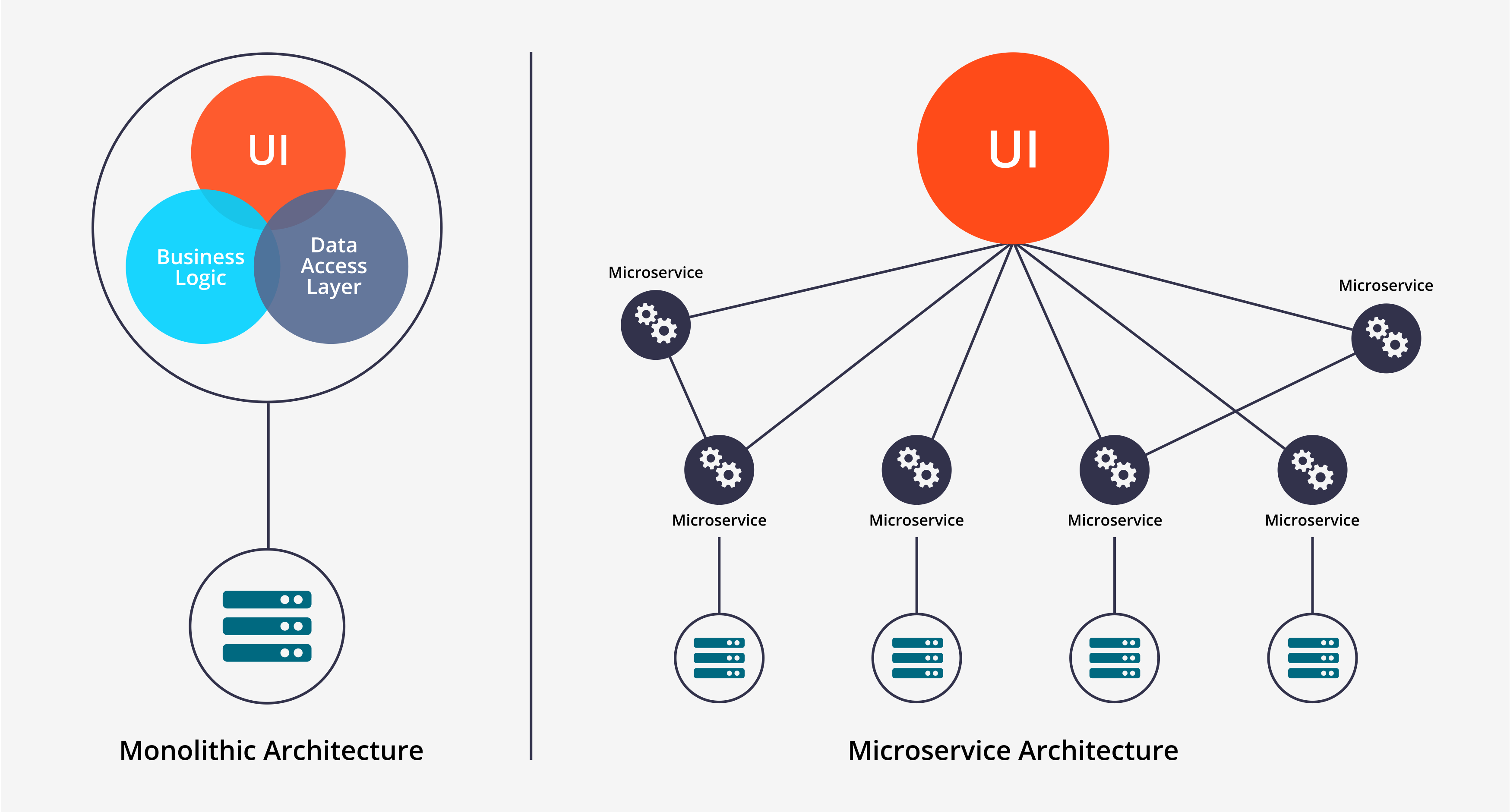
The goal is that teams can bring their services to life independent of others. Loose coupling reduces all types of dependencies and the complexities around it, as service developers do not need to care about the users of the service, they do not force their changes onto users of the service.
The microservice architecture brings the idea of decoupling functional parts of software applications into lightweight, deployable solutions, each having its own goal in the general ecosystem.
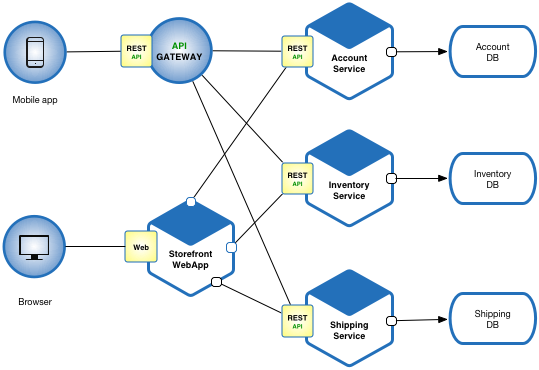
Microservices build in Python is considered to have an edge over other languages. Microservices in Python use a RESTful API approach. With this technology, it becomes easier to monitor the application since it is now broken into components.
There is a broad range of Python Microservices frameworks to choose from for your web application development. One of the most popular is Flask.
Multiple components
- Each service is a standalone component of its own
- Components deployment, replacing and removal is possible without compromising other services
- You have a relatively explicit component interface without tight data coupling
Business-oriented
- The services are built around business context and needs
- Each microservice is a product of its own
- Microservices necessitate having cross-functional teams that manage their respective products
Smart connection
- The services are usually connected by simple, ‘smart’ HTTP requests,
- The information flows through ‘dumb’ pipelines.
Decentralize everything
- Each service has its own resources and data storages
- Naming decisions can be different across the system
- You need to implement Data Transfer Objects (DTOs) for communication.
Let it fail
- Microservices must acknowledge that other services may fail
- Service failure is common due to availability issues triggered by, for example, connection problems, server downtime, and the like.
UML Diagrams
Microservices are just components (distributed components, not the architecture style per se) that have a clear provided interface.
As such, they should be represented in UML using the Components Diagram, with:
- Deployment diagram, to highlight its infrastructure and nodes used
- Sequence or activity diagram to highlight its aspects in relation to other Microservices or needed dependencies
- Package diagram to give a broader/clear overview of the Microservice organization and dependencies of other Microservices in the architecture solution.
When to Use Microservices?
Ultimately, any size company can benefit from the use of a microservices architecture if they have applications that need frequent updates, experience dynamic traffic patterns, or require near real-time communication.
Who Uses Microservices?
Social media companies like Facebook and Twitter, retailers like Amazon, media provider like Netflix, ride-sharing services like Uber and Lyft, and many of the world’s largest financial services companies all use microservices.
Flask demo
You can build a Microservice architecture with Flask.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# Import
from flask import Flask
import platform
# Flask App
app = Flask(__name__)
# Start point - Hello KEA
@app.route('/')
def hello():
return 'Hello KEA!'
# Check the operation system of your computer
@app.route('/oscheck')
def oscheck():
my_os = platform.system()
return 'Your operation system is: ' + my_os
# NoSQL Data
@app.route('/nosqldata')
def nosqldata():
return 'Test NoSQL'
# NoSQL Data
@app.route('/mysqldata')
def mtsqldata():
return 'Test MySQL'
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=80)
FastAPI Demo
FastAPI is a modern, fast (high-performance), web framework for building APIs with Python 3.6+ based on standard Python type hints.
The key features are:
- Fast: Very high performance, on par with NodeJS and Go (thanks to Starlette and Pydantic). One of the fastest Python frameworks available.
- Fast to code: Increase the speed to develop features by about 200% to 300%. *
- Fewer bugs: Reduce about 40% of human (developer) induced errors. *
- Intuitive: Great editor support. Completion everywhere. Less time debugging.
- Easy: Designed to be easy to use and learn. Less time reading docs.
- Short: Minimize code duplication. Multiple features from each parameter declaration. Fewer bugs.
- Robust: Get production-ready code. With automatic interactive documentation.
- Standards-based: Based on (and fully compatible with) the open standards for APIs: OpenAPI and JSON Schema.
Install
You have to install FastAPI and Uvicorn using pip:
1
python -m pip install fastapi uvicorn[standard]
When you have installede fastspai and uvicorn, its time to start the uvicorn server
1
uvicorn main:app --reload
It is running on your localhost and port 8000 - 127.0.0.1:8000
Very simple Python code - main.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"message": "Hello Kea"}
@app.get("/nosqldata")
async def root():
return {"message": "NoSql Data"}
@app.get("/mysqldata")
async def root():
return {"message": "MySql Data"}

Interactive API Documentation
Now open 127.0.0.1:8000/docs in your browser.
You will see the automatic interactive API documentation provided by Swagger UI:
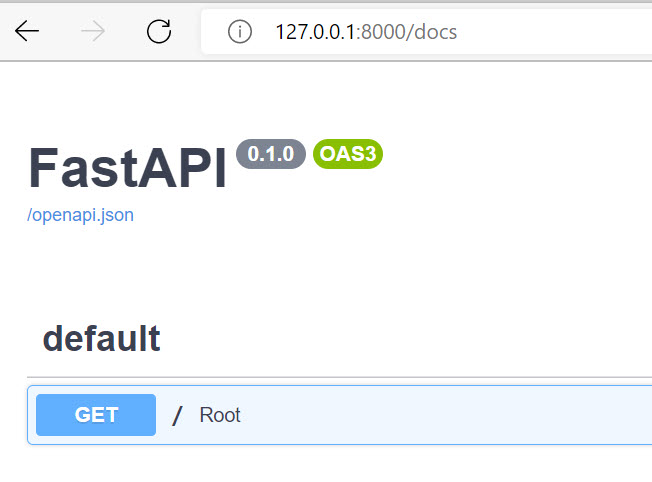
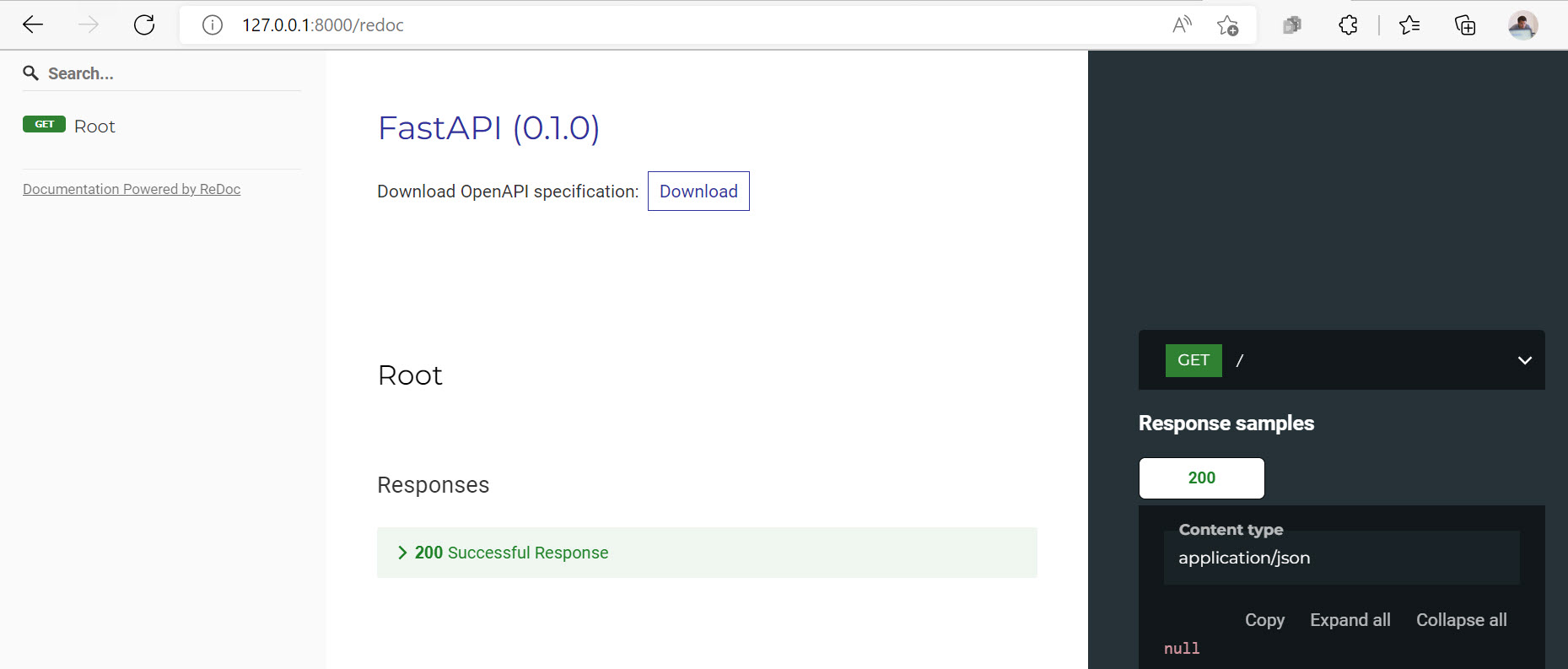
Or you can check the Alternative Interactive API Documentation.
Open 127.0.0.1:8000/redoc in your browser.
Resources
- Martin Fowler’s microservices article
- microservices.io
- fastapi.tiangolo.com
- Flask