Docker - Virtual Machine Azure
We are going to install Docker on your Azure Ubuntu Virtual Machine.
Connect
You need to connect via SSH to the Virtual Machine:
- IP adresse
- Username
- Password
Install Docker on Ubuntu
When connected to the Virtual Machine, we can start the Docker Installation.
Update the system
1
sudo apt update
Install Docker with apt
1
sudo apt install docker.io
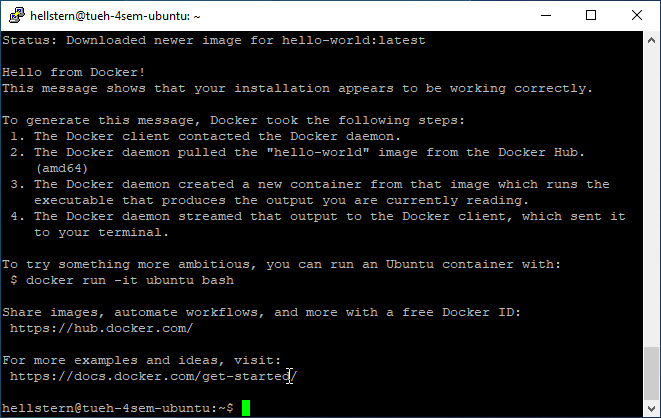
Verify that Docker is installed
1
sudo docker run hello-world
Your first Docker application
To create your first Docker application, you need to create a folder and move to the folder:
1
2
mkdir myfirstapp
cd myfirstapp
You have to create the following two files:
- main.py - Python file that will contain the code to be executed
- Dockerfile - Docker file that will contain the necessary instructions to create the environment
main.py
We do not need a complicated Python file for this demo :-)
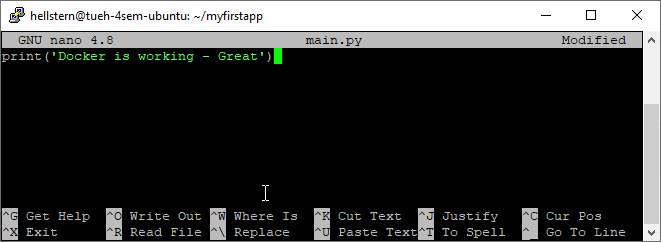
main.py
1
print('Docker is working - Great')
Simpel enough :-)
Create the main.py file on Ubuntu
1
nano main.py
This starts the Nano text editor, where you write the Python code
1
print('Docker is working - Great')
Save the main.py file
- CTRL X
- Y
- Enter
Dockerfile
A Dockerfile is a text document that contains all the commands a user could call on the command line to assemble an image.
A Docker file has NO extension!
FROM python:latest
COPY main.py /
CMD [ "python", "./main.py" ]
FROM python:latest
A dockerfile must always start by importing the base image. You use the keyword FROM to do that.
We want import the Python image, so you write python for the image name and latest for the version.
COPY main.py /
In order to launch your Python code, you must import it into your image.
For that you use the keyword COPY
The first parameter main.py is the name of the Python file on the host.
The second parameter / is the path where to put the file on the image. Here we put the file at the image root folder.
CMD [ “python”, “./main.py” ]
You need to define the command to launch when you are going to run the image.
Use the keyword CMD to do that.
The following command will execute python ./main.py
Create Dockerfile on Ubuntu
In the ssh terminal you write:
1
nano Dockerfile
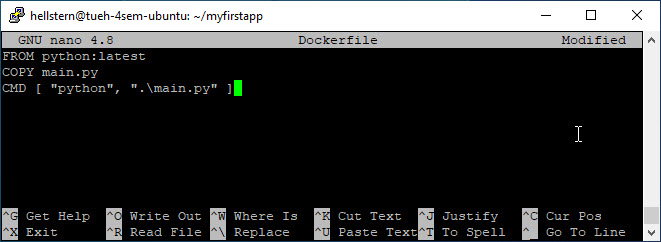
This starts the Nano text editor, where you write:
1
2
3
FROM python:latest
COPY main.py /
CMD [ "python", "./main.py" ]
Then you have to save the Dockerfile:
- CTRL X
- Y
- Enter
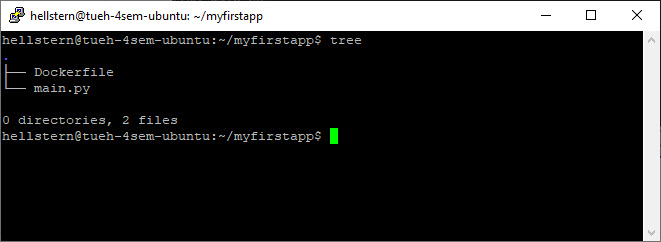
Now you could have a folder (myfirstapp) with 2 files:
Create the Docker image
When your code (main.py) are ready, and the Dockerfile is written, all you have to do is create your image to contain your application.
1
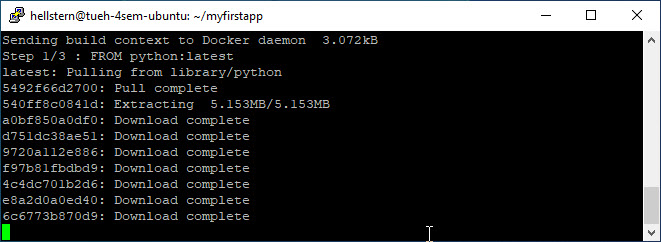
sudo docker build -t my-first-app .
The -t option allows you to define the name of your image. I’m using my-first-app but you can use what you want.
Note - Remember the . at the end
Run the Docker image
Once the image is created, your code is ready to be launched.
1
sudo docker run my-first-app
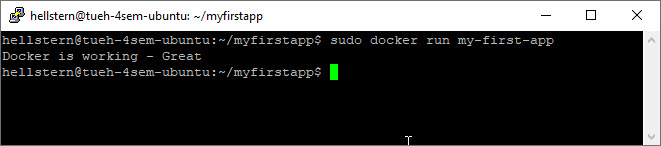
Remember: If you make any changes to the Python file (main.py) or the Dockerfile, you have to run the Docker build command agin
Commands for Docker
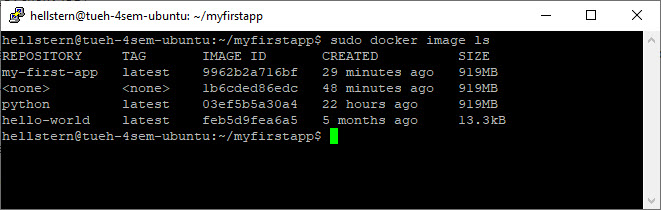
List your images
1
docker image ls
Delete a specific image
1
docker image rm [image name]
Delete all existing images
1
docker image rm $(docker images -a -q)
List all existing containers (running and not running)
1
docker ps -a
Change a container name at running time
1
docker run --name [container name] [image name]
Stop a specific container
1
docker stop [container name]
Stop all running containers
1
docker stop $(docker ps -a -q)
Delete a specific container (only if stopped)
1
docker rm [container name]
Delete all containers (only if stopped)
1
docker rm $(docker ps -a -q)
Display logs of a container
1
docker logs [container name]